Specialties

Addiction Treatment Specialties
Addiction affects each person differently, that’s why Livengrin has been providing the community from all different walks of life with personalized and specialized addiction rehab services since 1966. We offer recovery program specialties geared to helping first responders, healthcare professionals, assisting with DUI recovery and even gambling addiction services.
The road to recovery is less daunting when we go it together. That’s why Livengrin educates and empowers both patients and their peers. Our drug and alcohol addiction treatments provide the rehab and support patients need to achieve lasting recovery. We also offer drug and alcohol rehabilitation programs that help families and employers learn how to be a support system for a loved one or an employee struggling with addiction.
For more information on addiction treatment services at Livengrin call 215-638-5200 today. Together we can overcome addiction.
Journeys
FAMILY MEMBER
If you’re a family member searching for help for a loved one.
We’ve Got You
WORKPLACE PROFESSIONAL
If you’re a workplace professional struggling with addiction.
We’ve Got You
FIRST RESPONDER (FRAT)
If you’re a first responder struggling with addiction.
We’ve Got You
Journeys

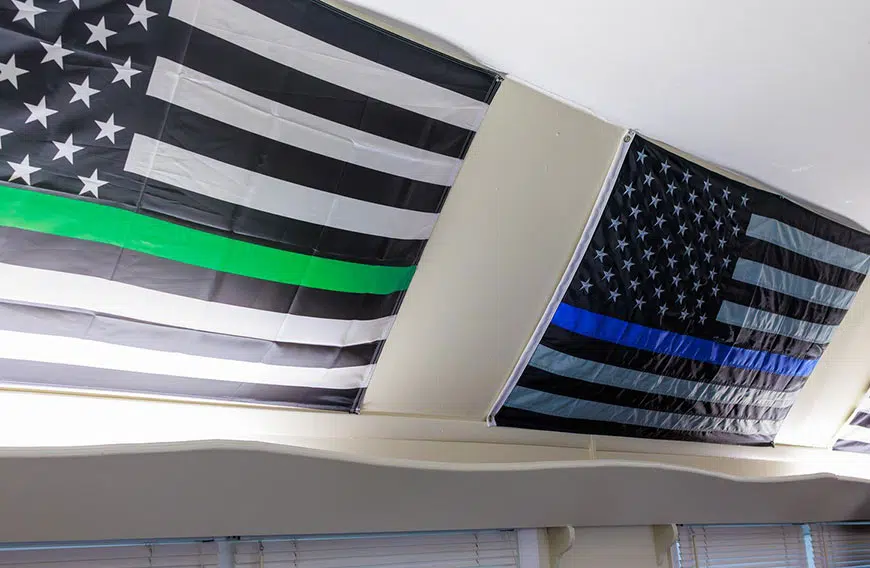
Individual
With our proven, evidence-based, treatment methods and personalized approach, Livengrin is the place where you’ll find the understanding and guidance to make lasting change.

First REsponder (F.R.A.T.)
The First Responders Addiction Treatment Program (FRAT) was one of the first programs in the area designed to treat the unique needs of emergency responders and veterans.
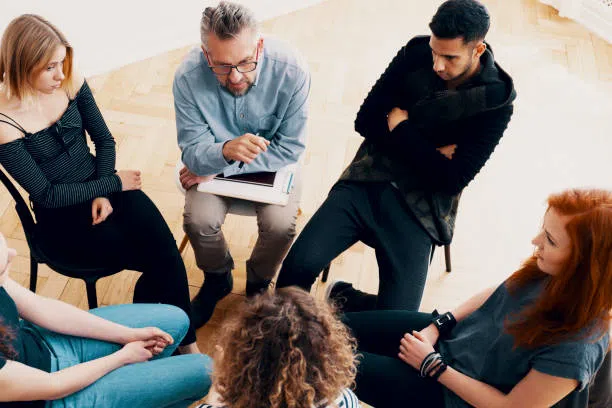

Workplace Professional
Livengrin has been a leader in helping workplace professionals find the support needed to focus on that difficult balance between careers and well-being.

Family Member
Our Family Support Program offers a range of services tailored to the unique needs of families, including couples group sessions, family support groups, and family education sessions.
Journeys

FAMILY MEMBER
If you’re a family member searching for help for a loved one.
We’ve Got You

WORKPLACE PROFESSIONAL
If you’re a workplace professional struggling with addiction.
We’ve Got You

FIRST RESPONDER (F.R.A.T)
If you’re a first responder struggling with addiction.
We’ve Got You